Over the next two months, the PathOS project training series will host free expert-led webinars designed to delve into the multifaceted impacts of Open Science—academic, societal, and economic—and methodologies for their effective assessment.
On 10 April 2025, Jessica Catalano will present the Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) Framework that CSIL developed as part of the project, illustrating its application in quantifying the impacts of Open Science. This session will explore how to evaluate Open Science’s benefits and costs, drawing insights from the project's case studies.
The one-hour free webinar, hosted on Zoom, will start at 10:00.
Register here to secure your spot: PathOS Training Session: Cost Benefit Analysis Framework for Open Science
Additional Training Sessions:
The full training series covers the different impacts of Open Science and how to effectively measure them. See the full list:
All webinars will be hosted on Zoom.
For more details and to register for these sessions, visit the PathOS Training Corner.
The European lighting fixtures market declined in 2023, following two years of exceptional growth. The total market value fell by 12% to approximately EUR 17 billion. However, despite this contraction, the market remains 6% larger than in 2018.
Market performance has varied across segments in recent years. During the pandemic, residential lighting saw stronger demand, but this trend has since reversed, with professional lighting recovering more robustly. Outdoor lighting has outperformed the market average, with steady annual growth of 1.5% since 2018. Several structural factors continue to shape the sector, including the European Union’s ban on fluorescent lamps, rising electricity costs, and the increasing adoption of smart lighting solutions. LED lighting now accounts for nearly 90% of the total market.
Looking ahead, the market is expected to remain challenging in 2024. Investment in residential construction across Europe is projected to decline by over 5%, though a modest recovery is anticipated in the following years.
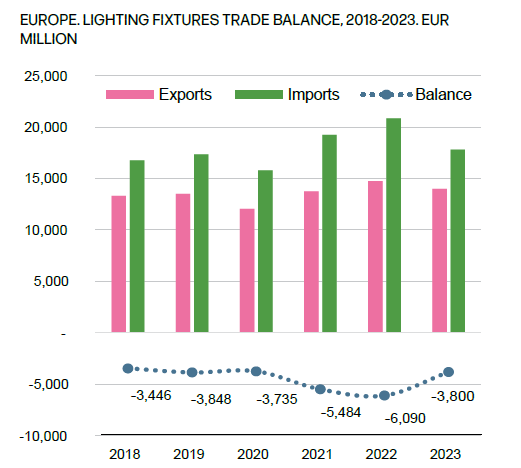
The European lighting fixtures trade saw a decline in 2023, with exports falling by 5% to EUR 14 billion and imports dropping by 15% to EUR 18 billion. This sharper decline in imports contributed to an improved trade balance, reducing the deficit from EUR 6.1 billion in 2022 to EUR 3.8 billion in 2023.
Germany remains Europe’s largest lighting fixture exporter, accounting for 19% of total exports, followed by Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, and Austria. Around 80% of exports remain within Europe, with North America serving as the most significant overseas market, followed by Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. Italy holds the largest net trade surplus in the sector, amounting to EUR 900 million.
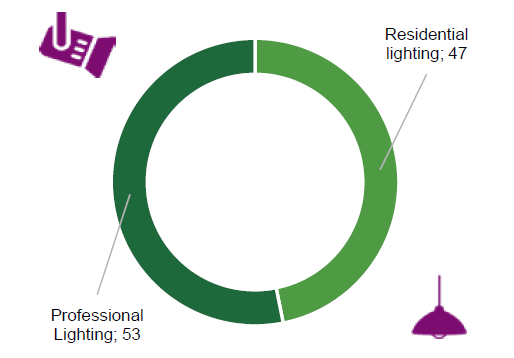
On the import side, the leading European markets for lighting fixtures are Germany, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Italy. In 2023, over 45% of European lighting fixture imports originated from the Asia-Pacific region, with China alone accounting for 43% of total imports. However, imports from Asia-Pacific saw a significant decline of 25.5% compared to the previous year. Professional lighting fixtures accounted for 53% of imports, while residential lighting fixtures made up the remaining 47%.
Technological advancements continue to reshape the lighting industry, with smart and connected lighting playing an increasingly prominent role. The market for connected lighting in Europe has expanded significantly, now accounting for 19% of the total market—double its share in 2019.
At present, connected lighting is more widely adopted in commercial, industrial, and outdoor applications than in residential settings. However, as smart lighting solutions become more user-friendly, adoption within the home lighting segment is expected to grow. These innovations not only enhance convenience but also contribute to significant energy savings through features such as programmable lighting systems, occupancy sensors, daylight harvesting, and integration with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Several major mergers and acquisitions took place in the European lighting industry in 2024, reflecting ongoing consolidation and technological integration:
These acquisitions highlight the sector’s evolving competitive landscape, with companies expanding their capabilities in connectivity, energy efficiency, and niche applications.
Despite short-term economic challenges, the long-term outlook for the European lighting market remains positive. The industry is set to benefit from increasing demand for energy-efficient and connected lighting solutions driven by regulatory requirements, sustainability concerns, and technological advancements. While 2024 may be a year of adjustment, CSIL forecasts indicate a return to growth in 2025 and 2026.
Read more on CSIL Report The European market for lighting fixtures, a detailed analysis of the lighting fixtures industry for 30 countries.
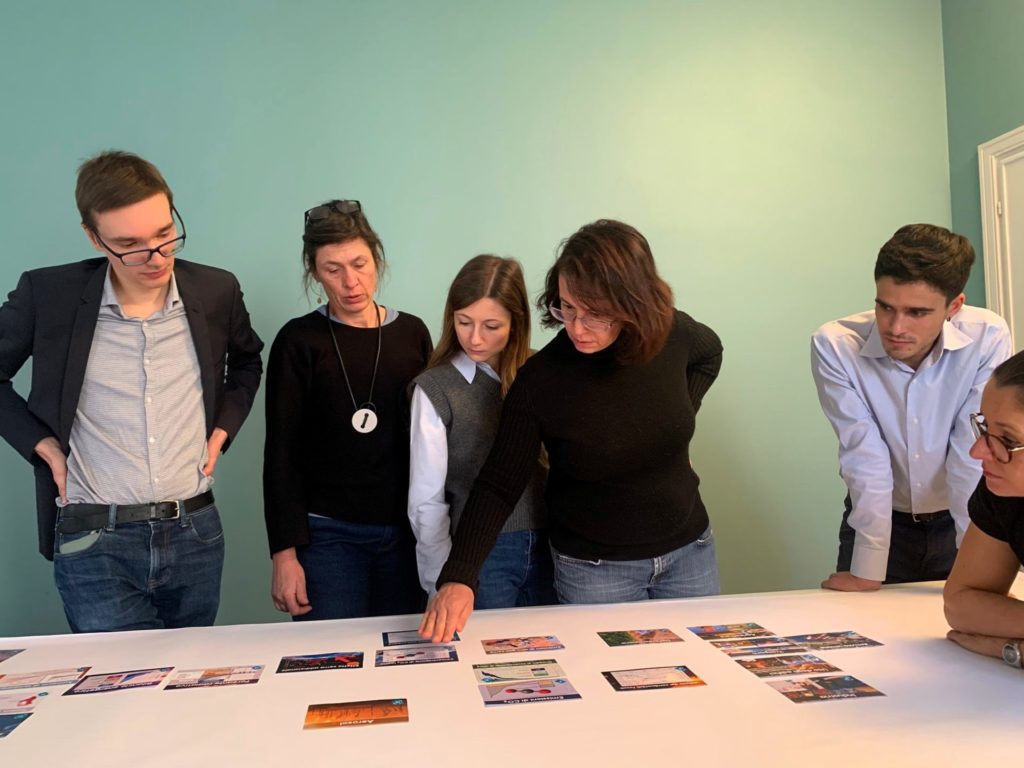
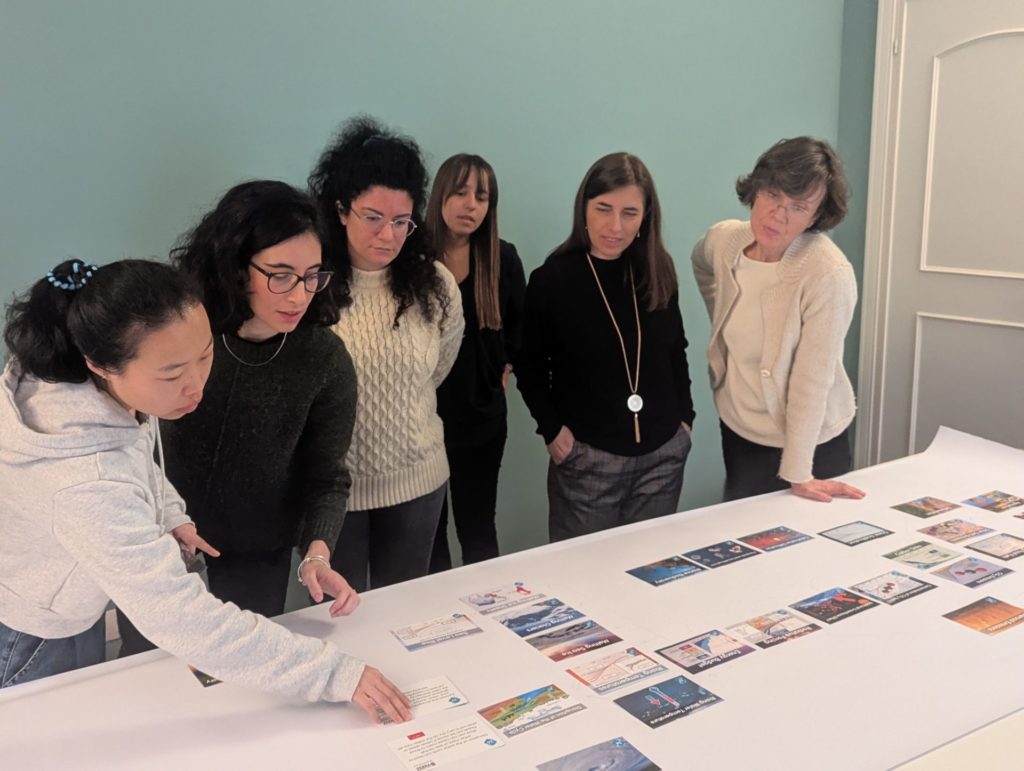
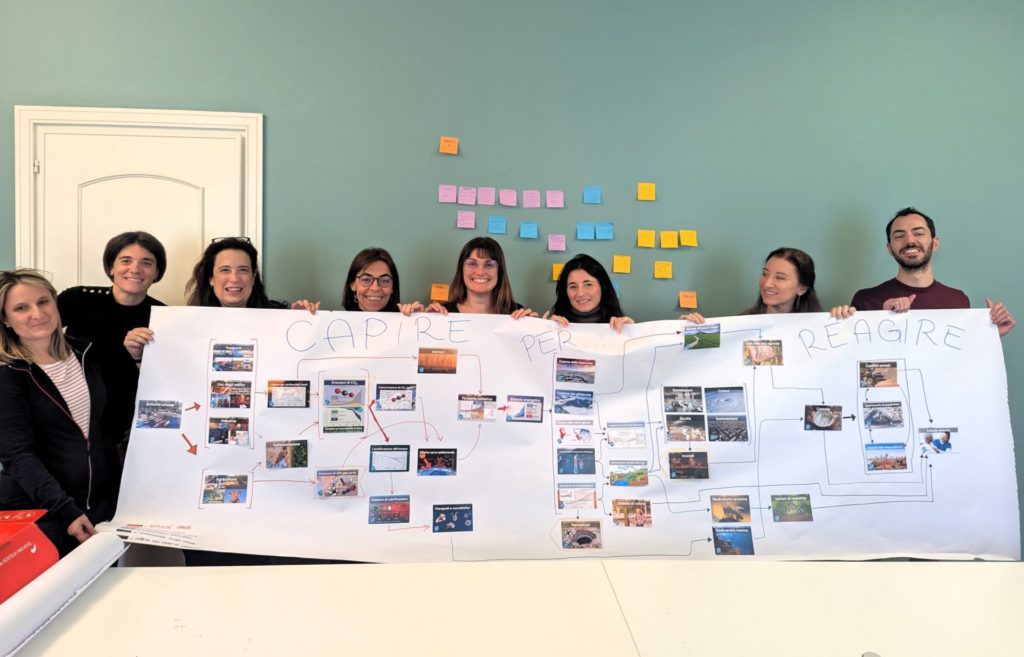
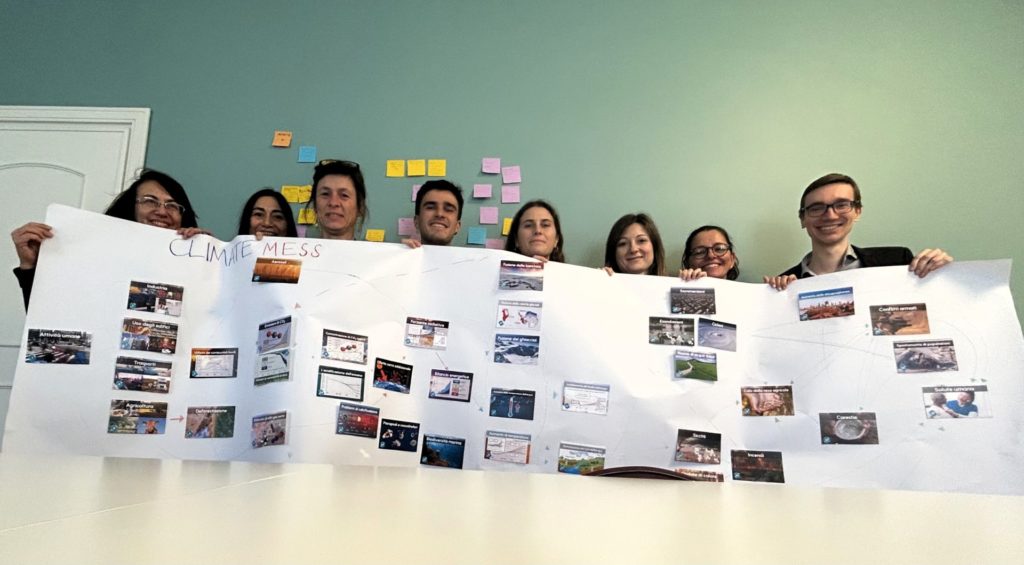
At CSIL, we recognise the importance of deepening our understanding of climate change and its implications for our work and daily lives. To foster awareness, collaboration, and action, we recently organised five Climate Fresk workshops, engaging our teams in an interactive experience that connects scientific knowledge with real-world impact.
The Climate Fresk is a globally recognised, science-based workshop that helps participants explore the causes and consequences of climate change through an interactive card-based methodology. Using knowledge from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), participants work together to build a visual representation of the complex relationships driving climate change, gaining a deeper awareness of environmental challenges.
Under the guidance of our colleague Louis Colnot, a Climate Fresk facilitator, these sessions provided a unique opportunity to enhance our collective understanding of sustainability issues while reinforcing teamwork and critical thinking. By discussing real-world implications and reflecting on our professional and personal roles in addressing climate challenges, CSIL team members were able to translate awareness into action.
Beyond its value in fostering environmental consciousness, Climate Fresk also serves as a powerful team-building tool, encouraging open discussion, collaboration, and problem-solving. Bringing together participants from different teams at CSIL, the workshops promoted cross-disciplinary exchange and strengthened internal cohesion, aligning with CSIL’s commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
Our engagement with Climate Fresk is part of a broader commitment to keeping climate awareness at the heart of our work. In recent months, our Reading Society meetings have sparked discussions on climate-related topics, enriching our perspective and reinforcing our dedication to sustainability. These workshops are another step forward in making environmental responsibility a practical and ongoing effort at CSIL.









In collaboration with Prognos AG, we have launched the survey on the future of Smart Specialisation Strategies (S3), part of an ongoing study commissioned by the European Commission’s Directorate-General for Regional and Urban Policy (DG REGIO). The consultation seeks to gather insights and feedback to evaluate and refine Smart Specialisation Strategies (S3) as a framework for driving regional innovation and economic transformation across the EU.
Smart Specialisation is a cornerstone of EU Cohesion Policy, aimed at empowering regions to identify and develop areas of competitive advantage through research and innovation. Your feedback will play a crucial role in shaping future policies, ensuring they address the real needs and challenges of regions, businesses, and innovation ecosystems.
The survey is open to a wide range of stakeholders, including:
Your perspective will help ensure the outcomes reflect the diverse needs and priorities across Europe.
The survey is hosted on the EU Survey platform and is available in multiple languages to ensure accessibility. It includes a mix of questions on:
Estimated completion time is approximately 15-20 minutes. Your responses will be treated confidentially and will directly inform the European Commission’s evaluation and recommendations.
The survey is open until 28 February 2025.
For any questions or further information, please contact Fabian Schmidt at fabian.schmidt@prognos.com.
Your privacy is our priority
Participation is voluntary, and all responses will be anonymised to protect your confidentiality. Data will be used solely for this study and processed in compliance with GDPR standards.
The global furniture sector faced a challenging year in 2024, shaped by economic uncertainty, geopolitical tensions, and shifting trade dynamics. According to CSIL’s World Furniture Outlook 2025, worldwide furniture consumption remained stable in current US dollars compared to 2023, though regional trends varied significantly.
Europe was among the hardest-hit regions, particularly Germany and France, where consumption declined. Despite a slowdown in inflation, economic uncertainty has continued to weigh on consumer confidence and spending. In contrast, Asia’s furniture industry has shown signs of resilience, with a gradual recovery in Chinese exports and a growing presence of Southeast Asian exporters.
From a trade perspective, 2024 was marked by complex challenges, including disruptions in maritime transport and heightened geopolitical risks. However, the global furniture trade still managed to grow by 2%, reaching an estimated USD 174 billion.
Economic conditions remain a key determinant of industry performance. According to the IMF World Economic Outlook (October 2024), global GDP growth is forecast at 3.2% for both 2024 and 2025, with emerging and developing economies outpacing advanced economies. However, the outlook is subject to several downside risks, including regional conflicts, potential economic slowdowns, financial market volatility, and shifts in international trade policies.
Political developments have further contributed to uncertainty. In 2024, elections took place in 76 countries, including key players in global trade, such as the United States, India, the United Kingdom, and members of the European Union. The impact of new policy directions on trade and economic cooperation remains a subject of close observation.
In 2024, global furniture production was estimated at USD 471 billion—unchanged from the previous year but lower than 2022 levels. While supply chain pressures have eased somewhat, full normalisation remains elusive, and the geopolitical climate continues to pose risks.
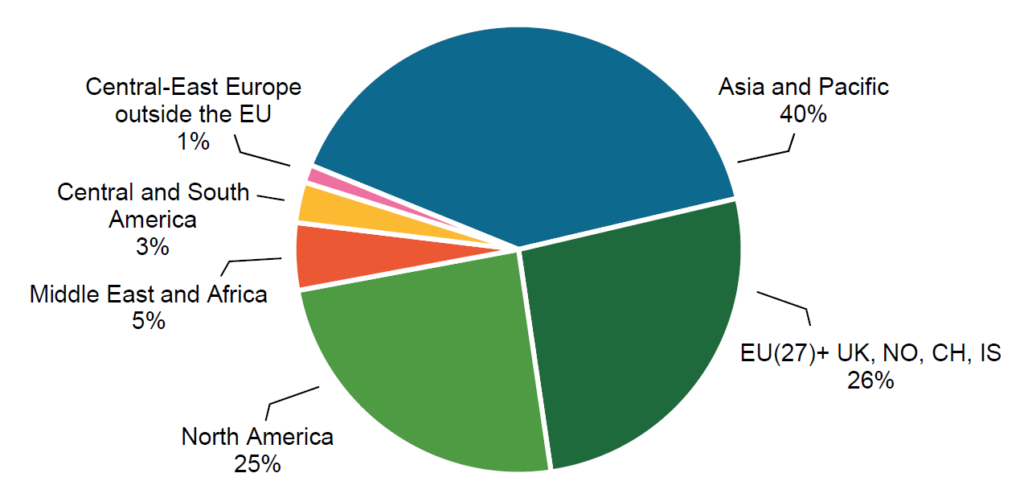
Asia and the Pacific accounted for more than half of global furniture production, with China remaining the leading producer and exporter. However, after a strong increase in exports in 2021, Chinese furniture exports declined in 2022 and 2023. Preliminary data suggest a modest recovery in 2024.
On the import side, the United States, Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Canada remained the top furniture importers, collectively accounting for almost half of total global imports. While US furniture imports showed a slight increase in 2024, demand in European markets remained subdued due to economic uncertainty.
Trade within economic regions has been a growing trend in recent years. In Europe (EU27, the UK, Norway, Switzerland, and Iceland), approximately 75% of foreign furniture trade occurs within the region. Similar patterns are emerging in Asia and North America, partly due to near-sourcing policies and shifting supply chain strategies. If protectionist measures become more widespread, regional trade integration could accelerate further.
Looking ahead, CSIL’s World Furniture Outlook 2025 projects that global furniture consumption will increase by 1.4% in real terms in 2025. However, several uncertainties could influence these projections, including trade policy developments, global economic performance, and ongoing geopolitical tensions.
While challenges persist, the industry continues to adapt, responding to evolving consumer demand, supply chain shifts, and regulatory changes. CSIL will continue to monitor these trends, providing evidence-based insights to support decision-making in the sector.
CSIL is proud to support the University of Milan (UNIMI) in the horizontal coordination of Spoke 2, a vital component of the CHANGES project. CHANGES, funded under the Italian National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNRR), aims to transform cultural heritage preservation and valorisation through technological innovation, sustainable practices, and digital transformation. Spoke 2 focuses specifically on intangible cultural heritage, addressing how it can be revitalised, preserved, and shared using cutting-edge tools like virtual and augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and big data.
Our role in Spoke 2 focuses on ensuring horizontal coordination among partners by enhancing impact, creating synergies, and promoting awareness of achievements. This ensures that the project’s valuable outcomes are effectively disseminated to the academic community, cultural institutions, and the broader public, thereby amplifying its societal impact.
This week, we had the honour of attending the national event in Rome, Patrimonio Culturale al Futuro: Sostenibilità Sociale, Innovazione Tecnologica, Trasformazione Digitale, an in-depth exploration of how Italian cultural actors are driving forward these ambitious goals. The conference highlighted the innovative solutions being implemented by the CHANGES project to bring new life to Italy’s cultural heritage while addressing broader societal challenges.

A highlight of the event was experiencing cutting-edge technologies in action. From virtual and augmented reality applications to AI-driven tools, the demonstrations underscored how these innovations are reshaping accessibility and engagement with cultural heritage. One of the most exciting moments was the CHANGES Awards, a dynamic poster session where participants presented their projects to an expert jury. The winning projects, chosen for their innovation, practicality, and potential impact, will serve as incubators, with their solutions refined and brought to market.
As the project enters its final year, we are eager to amplify its impact by ensuring widespread dissemination of results and laying the foundation for the long-term sustainability of the initiatives developed.
The question of whether large investments in fundamental science pay off has long intrigued economists, policymakers, and the public alike. Now, The Economics of Big Science 2.0 delves deeply into the socioeconomic impact of Big Science projects. This volume originates from research conducted in the recently concluded FCC Innovation Study (FCCIS), an H2020 project where CSIL developed the financial roadmap for the infrastructure project, including cost estimates, a financing plan, and a socioeconomic impact analysis. This publication sheds light on how groundbreaking scientific initiatives, such as those of the Future Circular Collider (FCC), can drive societal innovation and economic growth.

As one of the FCCIS project’s partners, CSIL is proud to have contributed to this publication, drawing from longstanding experience in the field. Our researchers authored three chapters in the book, offering insights into:
Awareness and Attitudes Towards Science: The Case of CERN: This chapter underscores the importance of public understanding and support for scientific research, particularly basic research, without immediate practical applications. Highlighting findings from a 2022 survey involving 8,443 responses from seven countries, the chapter reveals generally positive public attitudes toward CERN and particle physics while also discussing the polarization in perceptions and the societal value of curiosity-driven research.
Costs and Benefits of Open Science: Contributing to the Development of a Rigorous Assessment Framework: This chapter examines Open Science (OS) as a transformative force in research, promoting collaboration, transparency, and innovation. It proposes using Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) to systematically assess OS’s economic and social impacts. Linked with the PathOS project, in which CSIL is also a partner, the research further develops methodological guidance to map and quantify OS’s economic impact, suggesting a tailored CBA framework to compare the costs and benefits of OS.
Thinking How to Define and Measure Impacts of Research Infrastructures: This chapter addresses the growing demand to measure the broad impacts of Research Infrastructures (RIs) beyond the scientific domain, proposing a roadmap for assessing these effects. It identifies key challenges, including defining RI impacts and understanding their variation across disciplines. The chapter draws on recent discussions and practices in impact assessment to provide a structured approach for evaluating the societal contributions of diverse RIs.
The book launch was held at the Bozar Centre for Fine Arts in Brussels, where representatives from the science and policy sectors gathered to discuss the economics of Big Science. Silvia Vignetti attended and contributed actively to the discussions, where insights were shared on the sustainability and funding complexities of these scientific endeavours.
Speakers included Johannes Gutleber, Head of FCC Sustainability and Innovation Studies at CERN; Alexandr Hobza, Chief Economist of the European Commission, DG for Research & Innovation; Charlotte Mathieu, Head of the Industrial Policy and Space Economy Division at the European Space Agency; Prof. José Luis Martínez, Chair of the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures; Lidia Borrell-Damian, Secretary General of Science Europe; Riccardo Crescenzi, Professor of Economic Geography at The London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE).
The Economics of Big Science 2.0 is freely available in Open Access format. Published by Springer Nature, it invites academics, policymakers, and the public to explore how large-scale research projects enrich societies economically and intellectually.

According to a recent article by CSIL Market Research experts, the European furniture industry is still in the early stages of digital transformation, with few leading furniture manufacturers that fully integrate digitalisation in their processes.
CSIL’s research shows that for most furniture manufacturers surveyed, key digital innovations such as the Internet of Things (IoT), additive manufacturing, 3D printing, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are either in progress (60%) or just starting (10%). Only 20% of the companies have developed an advanced or fully integrated digital transformation roadmap.

A significant disparity exists between the availability of digital technologies and their widespread adoption in the European furniture industry. This gap is mainly due to challenges in acquiring the necessary skills, limited knowledge about new technologies, and a managerial culture that is not always ready to change. However, in the medium term, investments in digital transformation are expected to increase rapidly, doubling their share of the company’s turnover, according to the CSIL sample. These investments are expected to focus on integrating digital solutions across business areas, moving towards the concept of the “smart factory.” Smart products, too, will play a key role, with market shares projected to grow at a double-digit pace through 2030.
Key areas of digital investment include cybersecurity, cloud computing, and robotics. Both cybersecurity and cloud computing align with the EU’s Digital Decade Policy Programme, which aims for 75% of EU enterprises to adopt cloud services, big data, and AI by 2030.
Among the emerging technologies, artificial intelligence stands out for its diverse applications. AI is being used to optimise production processes and enhance service offerings in the furniture sector. Machine learning algorithms, for example, analyse consumer data from social media to identify and predict popular product trends. This allows companies to customise offerings, meet individual customer needs, and develop new, innovative materials.
Read the full article on World Furniture Online.
CSIL is proud to announce the launch of its Gender Equality Plan (GEP) 2024-2026, a strategic initiative designed to foster gender equality and promote an inclusive organisational culture. Aligned with guidelines from the European Commission and the European Institute for Gender Equality (EIGE), the plan ensures compliance with both EU and national legislation, marking a significant milestone in CSIL’s commitment to social justice and non-discrimination.
A New Chapter in CSIL’s Commitment to Equality. Building on our longstanding values of fairness, transparency, and social responsibility, and previous work on gender equality, the plan consolidates CSIL’s approach to inclusion. It addresses key organisational areas to enhance equality in the workplace, aligning with the organisation’s mission to contribute to socio-economic development through research.
Four Key Focus Areas. The plan focuses on four strategic areas identified as critical for promoting gender equality at CSIL.

Our ongoing efforts are designed to ensure that all employees, especially women, continue to thrive in an environment that upholds inclusivity and combats stereotypes. This is crucial for maintaining a healthy and innovative workplace.
CSIL’s Dedication to Diversity and Innovation. CSIL believes that diversity and inclusion are not just human rights but also powerful drivers of innovation and growth. As a research organisation, we know that gender equality improves decision-making, fosters creativity, and enhances productivity. With the majority of our workforce and leadership being female, our efforts now focus on sustaining and building upon the positive work environment we have cultivated.
Implementation and Continuous Monitoring. A dedicated Working Group has been appointed to oversee the GEP’s implementation, ensuring continuous progress and improvement. Specific actions, measurement criteria, and objectives have been outlined for each area, with periodic reviews set to monitor the impact of our initiatives.
The Gender Equality Plan is available online in a web version. For further details or to request the full version, please contact us.
Chiara Pancotti and Matteo Pedralli contributed to a ZEW’s discussion paper titled “The Recovery and Resilience Facility: Key Innovations and the Interplay With Cohesion Policy”, which originates from the study conducted for DG ECFIN “Supporting the Mid-term Evaluation of the Recovery and Resilience Facility” in 2023-2024.
With the aim of contributing to the ongoing discussions on the future of the post-2027 Cohesion Policy, the paper delves into the functioning of the Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF). It examines the interplay between the RRF and CP, illustrating their respective governance structures, the key strengths of the RRF, the main obstacles to its implementation, and the interaction between the two instruments. The chapter concludes that the RRF can provide at least two sources of inspiration for the future of CP and EU public investment policies: the performance-based payment mechanism and the link between reforms and investments.